Remote Monitoring of Processes in IIoT Applications Using LTE Routers
Industry 4.0 is the integration of machinery and systems in a way that allows for the collection of all data on production, infrastructure and finished products. A large amount of data collected on an ongoing basis allows for an optimization of the production process in real time. Process data is collected from many devices and sensors. It is also advisable to monitor the machines and equipment already delivered to the customer, operating parameters and technical condition of which can also provide valuable data to improve the quality and efficiency of production. The analysis of a large amount of data allows for a better understanding of the process and its optimization, which increases the efficiency, quality and effectiveness of the production process.
The data transmission technologies used for data transmission are wired, fibre optic and radio (wireless) transmission. Wireless communication is used in the following applications:
• Monitoring, measurement and control of production processes
• Remote programming of PLCs, HMI panels
• Video monitoring
• Control of machine parameters working in remote and hard-to-reach locations (e.g. pumping stations, power generators, wind farms etc.)
In the above-mentioned areas, the most popular are systems based on GSM networks. In the case of Advanced LTE standard, the bandwidth can reach realistically even several hundred Mbps with high stability and low transmission costs. In order to establish a connection through a cellular network, GSM routers are used, i.e. equipment which controls (routes) the movement of traffic over the network. They allow you to redirect network traffic between different subnetworks and different interfaces: LAN, Wi-Fi, GSM. These devices need a static or dynamic IP address for their work. Encrypted protocols and VLANs are used to ensure security. It is not recommended to use simple port forwarding without encryption, because this solution is susceptible to interception of transmission and control of devices by unauthorized persons. It is recommended to use VLAN based on a protocol that ensures privacy and security of transmission, for example Open VPN. This is an open source software package for creating virtual private networks developed for Unix operating system. Open VPN authentication is done with keys or a username and password. The following VPN tunnel modes are possible: Router mode and Bridge mode. In Router mode, the IP address on both sides of the tunnel must be different, preventing possible repetition of IP addresses across the entire private network. In this mode, it is possible to manage the assigned IP addresses within both segments, but at the same time the communication in layer 2 (e.g. broadcast or multicast frames) will not pass through this tunnel. In Bridge mode, this problem does not occur, because the networks are bridged, i.e. they have the same address, which allows for full communication as in a physical LAN, but bridge mode is more difficult to configure. There is always a client and a server in both modes. The server role is to wait for the data from the VPN client on the defined TCP port. For this reason, the server must be publicly available, i.e. it must have a permanent public IP address. It is necessary to equip the routers with a SIM card with a static and public IP address to configure the Open VPN server. Unfortunately, data transfer using a SIM card with a static IP address is significantly more expensive than non-public dynamic addresses.
Self-configuration of the server and VPN client, the need to provide static IP addresses may be associated with some difficulties and costs. In such a situation, a better solution consists of routers equipped with Cloud Server service, which allows for secure and encrypted data transfer without the need to provide static IP addresses. An example of such a device is the ARS-2131-LTE router (Figure 1) operating in Advanced LTE mode with Cloud Server VPN service. With the Open VPN server running in the cloud, all the above problems are solved, and the configuration is simple and possible in a few steps. The device has the functionality of an IoT gateway and allows for a remote access to the supervised system from anywhere in the world. The working principle is shown in Figure 2. Security is ensured through an encrypted VPN tunnel using 2048 bit or 4096 bit secure encryption keys.
Simplicity of use and low costs of data transfer are undeniable advantages, but security issues must not be overlooked. The combination of IT corporate systems (IT) and industrial data transmission networks (OT) creates a layered structure, in which each level has different specifics, requirements and architecture of connections to the outside world. As a result, the protection of such a network resembles multi-level protection of a strategic object and is sometimes called “Defence in Depth” or “Castle Approach”. It is divided into three aspects – physical, technical and administrative. A well-designed industrial network security system requires tools to force proper user behavior, monitor and detect changes or malicious code installation, react quickly and restore business continuity in the event of an attack. One of the more widely known standards is IEC 62443. It lists a number of potential problems that should be taken into consideration when designing network equipment, so that you can talk about safe equipment. GSM routers should provide security at layer 3 and 4 levels.
To sum up, GSM routers allow for a remote access to systems using cellular networks. They allow to achieve transmission speeds of up to several hundred Mbs using an encrypted VPN channel, which allows to remotely program and solve problems associated with the operation of remote devices (PLCs, control and measurement modules), monitor the technical infrastructure (HMI, SCADA, IP cameras). Remote access to PLCs and other automation devices enables monitoring and remote assistance without the need for hours of travel to the facility.

Figure 1 (ARS-2131-LTE)
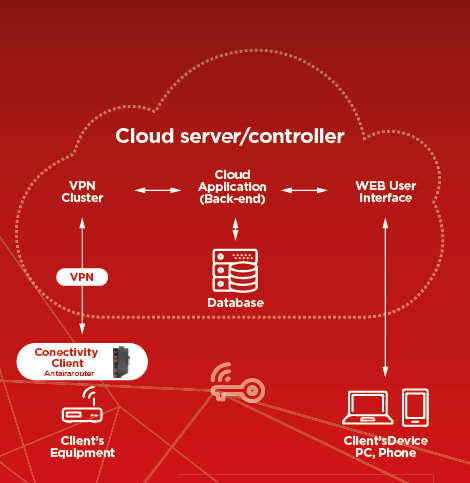
Figure 2 (IoT Cloud Gateway ARS-2131-LTE Operating Principles)
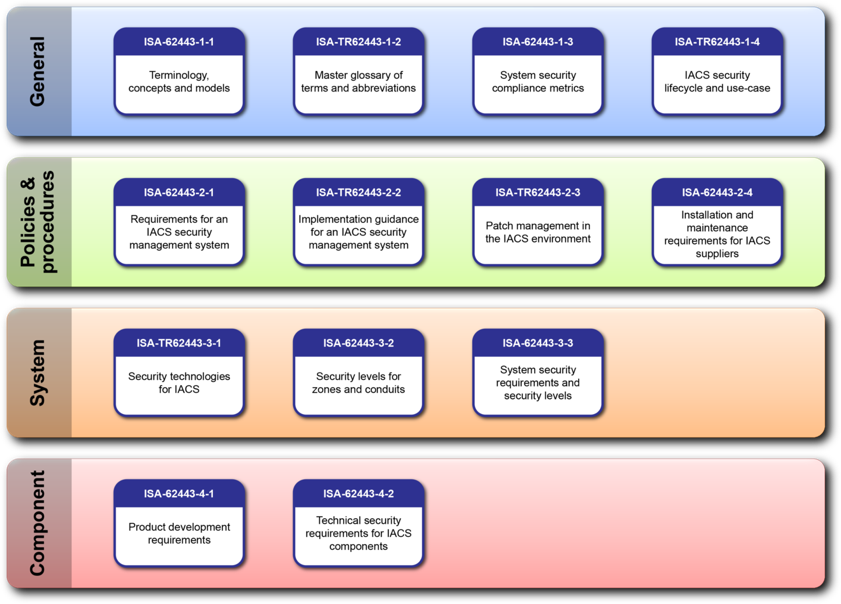
Figure 3 (Layer Structure of the ICS System – IEC 62443 Standard (ISA.ORG))