|
|
Security in Remote Monitoring Systems for IIoT Applications
Increasingly, machine manufacturers or automation system integrators look for solutions that allow them to easily and quickly monitor installed equipment and systems on-site. Such remote supervision allows to reduce implementation costs and offer a package of added services to control process parameters and anticipate possible faults before they occur. An important element is the security of data transmission, so that it is resistant to attempts to interfere with the operation of the monitored system, ensuring the integrity and reliability of transmitted data. So let's take a look at an exemplary implementation of the ARS and AGS router series from Antaira Technologies. The system allows free shaping of the monitoring system topology. Various process data or video streaming can be transmitted. An exemplary implementation is shown in Figure 1.
Advanced remote monitoring systems use routers that use VPN encrypted transmission channels and servers in the cloud. Such a solution allows to bypass the limitations imposed by the firewall or NAT, as well as allows to use static IP addresses on the side of the monitored device and surveillance station.
What affects the security of these solutions? We can list a number of norms and standards that systematize cybersecurity. The most popular are NIST 800-53, NERC CIP for power generation or IEC 62443. They give a number of recommendations for system designers, network component manufacturers, as well as users – defining a catalogue of good practices for safe industrial automation systems. System protection means resemble multi-level protection of a strategic object and are sometimes called “Defense in Depth” or “Castle Approach”. They are divided into three aspects – physical, technical, and administrative.
Physical security is ensured by securing the infrastructure, especially cloud servers and end point routers. The locations of the servers are protected against third party interference. Both hardware and software are constantly updated, and their operating status is monitored on an ongoing basis. Applications are optimized and validated for safety. Another important element is to secure the router by introducing multiple access levels, forcing strong periodically changed passwords, analyzing packets in terms of their structure and filtering, rules and QoS rules. An important element is also the self-diagnosis and implementation of the Watch-dog timer, allowing for an automatic reset in case of communication problems. From a technical point of view, an important element is to secure the transmission channel. Confirmation of compliance with these standards are ISO 27001 and AICPA safety certificates. Let's take a look at one of the most secure VPN implementations using the Open VPN protocol. We can distinguish three levels of security when establishing communication between end points:
• Authentication – Checking if the server and client are the ones we actually want to connect to. This can be done with a login and password or with authentication keys. The second method is safer and is used in industrial systems. This prevents someone from obtaining an authorization element (e.g. a password) or trying to impersonate a VPN server. Thanks to TLS, a server always has its own key, issued certificate and CA certificate. On the client's side, there must also be a copy of the relevant CA certificate. The authentication must end successfully on both sides – the server (cloud) and the client (router).
• End Points Authorization – Verification, whether a given client has the right to access the VPN network. As above, it can be done on the basis of a password - a set of keys.
• Cipher – Consists in encrypting the transmission in such a way that it cannot be read and modified.
There are also other mechanisms that are designed to increase the security of the transmission. In OpenVPN, there is a keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) mechanism that uses a separate key to sign each control packet when starting transmission. Data that is not properly signed with such a key is automatically rejected. Another form is multicomponent authentication, where an interesting and secure implementation is AWS MFA (Amazon Multi-Factor Authentication).
For secure communication, a method was needed to effectively authenticate its participants and ensure its integrity. For this purpose, public key infrastructure has been created, i.e. a set of elements enabling the creation of keys, certificates, their signing, revocation and verification. The entire service is handled by trusted companies called Certificate Authorities. When creating a VPN connection, the cloud server generates a key pair consisting of a private key and a public key, together with a request to sign a certificate (CSR). CSR is an encoded text file that contains the public key and other information that will be included in the certificate. After the CSR is generated, the server sends it to the certification authority, which checks whether the information contained therein is correct and if so, digitally signs the certificate with a private key and sends it back. In addition, it is worth paying attention to the security – the certificate's purpose. Thanks to this, even if we have a certificate signed by our CA, but it is not a server type, we will not run our own server. This makes it impossible for a client with a valid client certificate to impersonate a cloud VPN server. The authorization process ensures that only authorized devices can establish communication and that the transmission is encrypted and protected against modification by third parties. The authentication and authorization processes are as follows:
• A router connects to a server and presents its CA-signed certificate, the server verifies its correctness with the CA certificate.
• The server presents its CA-signed certificate and the client verifies it on the basis of the CA certificate.
• The server encrypts the transmission to the client with a public client key and the client decrypts it with their private key.
• The client encrypts the transmission to the server with a public server key and the server decrypts it with its private key.
• The server uses its private key to sign (ensure integrity and certainty of origin) data to the client, and the client verifies it with a public server key.
• Client signs data to the server with their private key and the server verifies it with the client's public key.
Remote monitoring systems allow you to control any machine or system from anywhere in the world. The manufacturer or integrator can monitor the operating parameters of a system installed in a place hundreds or thousands of kilometres away in real time. This allows for remote optimization and early detection of problems without the need to send a service technician on site. The security of such solutions is one of the key elements and is ensured by multi-level hardware and software protection. Current solutions provide a high level of security with easy and cheap implementation. Browse Antaira's website to learn more about our wireless routers and Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches.
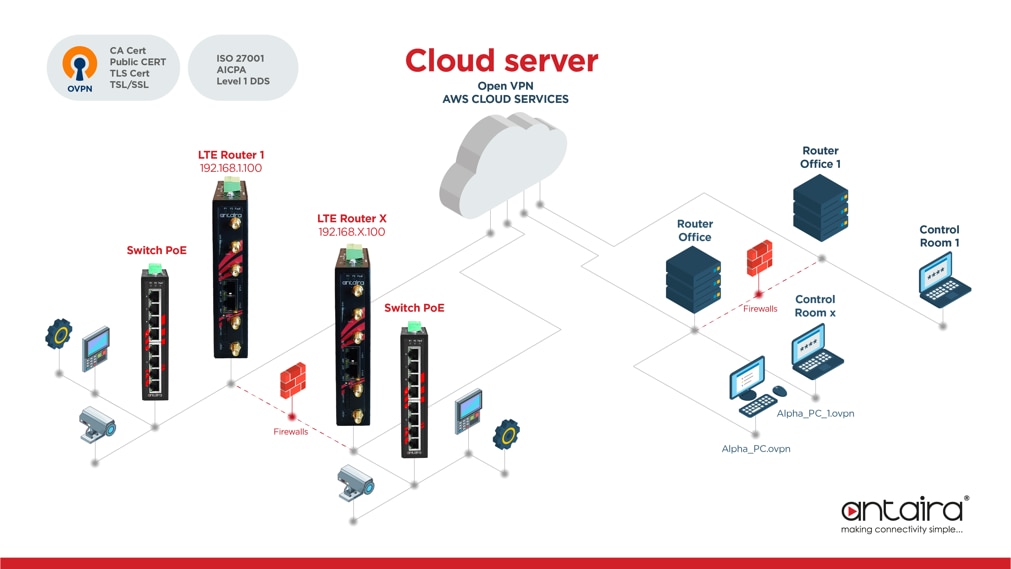
Figure 1 (Surveillance and Monitoring System)
The article uses information from https://openvpn.net
|
|
|
|